Author: Bothaina Alsobai 1, Dr Dalal Aassouli 2
1 College of Islamic Studies, Hamad Bin Khalifa University.
2 College of Islamic Studies, Hamad Bin Khalifa University
Journal of Strategic Business 2025,
Submission received: 12 June 2025/ Accepted: 18 June 2025/ Published: 1 August 2025
Abstract
The advancement of digital transformation influences future retail banking and emerging customer expectations.
This review aims to provide a better understanding and frame digital transformation strategies in global retail banking. A systematic literature review (SLR) of the existing methodologies was conducted to provide secondary insights on how artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, open banking, cloud computing and cybersecurity enhancements have been adopted.Therefore, 20 relevant studies were selected and analysed using the PRISMA framework. Findings revealed that customer experience, operations efficiency can be improved, as well as financial inclusion can be brought about by digital transformation. However, banks have to confront constraints such as legacy systems, regulatory compliance, cybersecurity threats and organisational resistance.This review analyses how AI helps in improving digital transformation strategy by strengthening cybersecurity measures, enhancing collaboration with the FinTech and ultimately integrating AI-driven decision making. Future research can further explore the emerging technologies, including quantum computing as well as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC), to minimise threats of being hacked as well as to improve digital banking security and financial stability.The findings of this review are valuable for the banking institutions, policymakers, and researchers to navigate the rapidly emerging landscape of digital transformation in retail banking.
Keywords: Digital Transformation, Retail Banking, FinTech, Financial Innovation, Cybersecurity, Artificial Intelligence.
© The Author(s) 2025. Open Access
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material.You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third-party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit:
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
1. Introduction
Due to digital advancement, retail banks faced a critical imperative to improve customer experience, operational efficiency and the ability to adapt rapidly changing market conditions [1]. Therefore, traditional banks are leveraging digital technology to offer seamless, personalised, and convenient banking services as demand increases from consumers [2, 3]. Bank of America introduce an artificial intelligence (AI) powered virtual assistant embedded in a mobile application that notifies users regarding bills, updates credit score, gives budgeting advice in real time and in a very simple, conversational language [4, 5]. Moreover, Emirates in UAE offers an instant account opening, smart budgeting tools and lifestyle-driven rewards with the help of AI and behavioural analytics on a millennial-based digital-only banking platform launched under the name of Liv [6].
At the same time, Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) has adopted biometric authentication, including voice and facial recognition, that allows customers not only to enjoy the conveniences of safe and secure account access and transactions with no passwords available, but also to maintain the security of their accounts [7]. However, recent studies have shown that being digitally transformed significantly improves customer satisfaction through offering online and mobile banking services in terms of higher convenience and availability [8, 9, 10]. The use of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), BDA and cloud computing allows banks to simplify operations, cut costs, eye risks, among others [11] [12] [13]. According to Hosen et al. [14], Naimi-Sadigh et al. [15], and Zhao et al. [16], banks make better decisions and facilitate customers according to their needs by incorporating technologies which allow for efficient analysis of customer data, thus leading to improved decision making.
In recent years, rapid technological advancements and the emergence of FinTech companies that bring innovative and user-friendly financial solutions to people have made great changes to the global banking sector. To remain relevant in an increasingly digital future, traditional banks are working to integrate this technology into the current banking environment, to better serve their customers and grow the client base in an attempt to keep up with the rise of digital demand for faster and more personalised services [17, 18]. Ofosu-Ampong’s report reveals that the COVID-19 pandemic drove the industry towards digital adoption, and during the period, many banks reported increased online transactions and digital involvement [19]. As a result, traditional banks have undertaken the evolution of rethinking their traditional business models and investing in digital capabilities. According to Ononiwu et al., over 60% of the banking
institutions are either starting or implementing digital transformation projects, which demonstrates the perception of one industry of necessity in agility in the world of cautiousness [20].
Purpose and Objectives
The major purpose of this review is to evaluate digital transformation strategies of retail banks all over the world. This SLR reviews specific objectives involving analysis of how various banks in different regions have adopted the digital opportunities to improve their reach, the effect on customer satisfaction, loyalty and overall experience and the key challenge to come up with appropriate improvements. Digital transformation in the current times involves open banking, whereby customers can share their data with third-party providers for improved services, mobile banking whereby customers make more choices through their mobiles, cloud computing for scalability and cost making, and personalisation through data analytics for detailed banking experiences [21]. Although there is a great number of research studies conducted on digital transformation in banking, the studies usually discuss fragmented elements such as customer experience, technology adoption, or operational efficiency.
There are few studies that present a thorough, global synthesis of these dimensions to understand how digital transformation strategies affect the retail banks in their totality which resulting in a huge knowledge gap in the field. This SLR not only consolidates existing views but, at the same time, discovers patterns and obstacles, as well as the successful practice of others in various settings. Moreover, this review is significant for policy makers, bank managers and researchers to make informed decisions that lead to innovation, better customer experience and eliminating the barrier of implementation in the early days of the digitally banking environment [22, 23]. There are also issues related to facilitating digital initiatives, such as the culture of the organisations, as changing culture is essential for their successful transformation efforts [24, 25, 26].
Research Questions
These research questions are proposed because the study aims to systematically evaluate the digital transformation strategies in retail banking.
-
RQ1 What digital transformation strategies are used by retail banks globally?
-
RQ2 How do these strategies create value for customers?
-
RQ3 What challenges hinder successful implementation?
-
RQ4 How can these strategies be improved?
2. Methodology
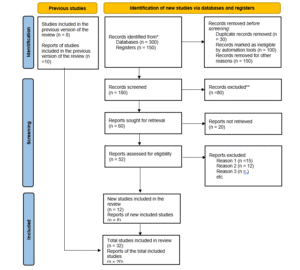
SLR applies the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) framework for maintaining rigorous review transparency. Systematic reviews need a structured approach and the PRISMA guidelines serve this need especially for synthesising existing knowledge about digital transformation strategies in retail banking [36].
2.1 Search Strategy & Databases
The study used an extensive search methodology to retrieve studies from 2015 to 2025. The study utilised the databases Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar and ScienceDirect and IEEE Xplore for its search. The chosen databases successfully covered academic literature in
both business and technology domains because of their broad scope. The suitable search terms used in the research included “digital transformation” alongside “retail banking” and “banking sector” variations to ensure extensive exploration of the subject area.
2.2 Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
This review included research papers which studied digital transformation specifically in retail banking because they were published after 2015. The research period was selected to observe modern digital banking trends and developments specifically. Only studies featuring retail banking sectors and direct connections to digital transformation remained, while investigations on other sectors were excluded. The selection criterion rejects research unless it analyses relevant contexts because studying relevant circumstances leads to meaningful insights [37].
2.3 Data Extraction & Synthesis Approach
Data extraction involved a systematic process where key information from each selected study was recorded. This included details on the digital transformation strategies employed, challenges faced by banks during implementation, and proposed solutions. The extracted data were then thematically categorised to facilitate synthesis. Thematic analysis is a widely recognised method in systematic reviews that allows researchers to identify patterns and themes across multiple studies [38]. By categorising the findings into strategies, challenges, and solutions, this SLR aims to provide a structured overview of the current state of knowledge regarding digital transformation in retail banking.
Table: Selected Studies
| No. | Author(s) | Title | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Abdullah, M. (2023) | The Cutting Edge Technologies in Computer Science: A Review | http://dx.doi.org/10.26483/ijarcs.v14i1.6945 |
| 2 | Adewumi, A., Ewim, S. E., Sam-Bulya, N. J., & Ajani, O. B. (2024) | Advancing Business Performance Through Data-Driven Process Automation: A Case Study of Digital Transformation in the Banking Sector | https://doi.org/10.53430/ijmru.2024.8.2.0049 |
| 3 | Ahmad, M. (2018) | Review of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) in Internet Banking and Mobile Banking | https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329034437 _Review_of_The_Technology_Acceptance_Model TAM_in_Internet_banking_and_Mobile_banking |
| 4 | Ahmed, G., Al Amiri, N., & Abudaqa, A. (2024) | Strategic Leadership and Economic Transformation: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) Model | http://dx.doi.org/10.70273/RSFK3414 |
| 5 | Al Faisal, N., Nahar, J., Waliullah, M., & Borna, R. S. (2024) | The Role of Digital Banking Features in Bank Selection | http://dx.doi.org/10.70937/faet.v1i01.10 |
| 6 | Alsemaid, O. M., Atri, P., Kande, S. K., & Lembhe, P. (2024) | Cutting-Edge Innovations in Technology and Security | https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id= 8KUbEQAAQBAJ… |
| 7 | Atabey, A. (2021) | Open Banking & Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS): A Delicate Turnout for the Banking Sector | https://www.proquest.com/openview/d9d274 3d7ea61b91cb6e45fc40c685b2 … |
| 8 | Bankuoru Egala, S., Boateng, D., & Aboagye Mensah, S. (2021) | To Leave or Retain? An Interplay Between Quality Digital Banking Services and Customer Satisfaction | https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-02-2021-0072 |
| 9 | Bellantuono, N., Nuzzi, A., Pontrandolfo, P., & Scozzi, B. (2021) | Digital Transformation Models for the I4.0 Transition: Lessons from the Change Management Literature | https://doi.org/10.3390/su132312941 |
| 10 | Best, J. (2018) | Breaking Digital Gridlock: Improving Your Bank’s Digital Future by Making Technology Changes Now | https://books.google.com.pk/…/KDdJDwAAQBAJ… |
3. Theoretical Framework
This study analyzes various established theories and concepts that form the foundational framework for examining digital transformation strategies in retail banking. These frameworks offer diverse perspectives that are essential for a comprehensive analysis. Specifically, the study integrates the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and the Resource-Based View (RBV) theory, along with insights from FinTech dynamics and digital market systems. Additionally, it takes into account geographical variations in the implementation and effectiveness of digital transformation strategies [39].
3.1 Digital Transformation Theories
Modern users adopt technology based on its perceived ease of use and usefulness, as outlined by the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) [40]. In the context of retail banking, this model proves valuable in explaining how customers engage with digital banking platforms [9]. Research indicates that consumers are more likely to adopt digital banking solutions when they perceive them as easy to use and beneficial, prompting financial institutions to enhance their digital service interfaces accordingly [41].
From a strategic perspective, the Resource-Based View (RBV) theory asserts that competitive advantage arises from internal resources and capabilities [42]. In retail banking, this theory underscores the importance of leveraging organizational assets—such as robust technological infrastructure and skilled human capital with strong customer relationships—to drive successful digital transformation initiatives [43].
Rane [44] further emphasizes that banks equipped with advanced data analytics capabilities are better positioned to understand and anticipate customer needs. This enables the delivery of personalized services, which fosters customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3.2 Role of FinTech and Digital Ecosystems
Digital advancement in retail banking depends heavily on FinTech organisations because they develop disruptive solutions which transform standard banking practices. Digital ecosystems comprised of banking institutions and FinTechs, and customers work together through networks to achieve better service delivery [45]. The linked network structure enables banks to deliver wider service offerings with better operational performance [46]. Financial institutions achieve superior client experiences through their alliances with FinTech firms, which enable them to implement AI and blockchain technologies throughout their business operations [47].
3.3 Comparison of Digital Transformation Strategies Across Different Regions
Strategic analysis of digital transformation reveals major neighbourhood-specific variations because of unique market traditions and regulatory frameworks, and shopping habits of residents. Western banking systems focus on omnichannel customer experience development, but emerging market institutions focus on mobile banking solutions to provide financial inclusion [48]. Operations of mobile banking technology demonstrate rapid growth thanks to Indian government initiatives, which accelerated digital financial inclusion among underserved people [49]. The Middle Eastern Nation United Arab Emirates, has oriented its digital transformation efforts towards complete technology integration, which simultaneously elevates both operational performance and client relationship quality [50].
4. Digital Transformation Strategies in Retail Banks
This systematic literature review brings together the key strategies, regional variations and emerging trends in digital transformation of retail banking as it is presented in the studies included in the review. There are several identified central strategies for the digital transformation of banks. Customer experience and accessibility of mobile banking have become a critical component in order to provide convenient and on-the-go financial services [51]. The other strategy, which is equally important, is AI-driven chatbots that personalise customer service and streamline operational efficiency through automation [52]. Being one of the prospective integration potentials into the banking transactions, blockchain is recognised as a potential pro to security and transparency of banking transactions upon payments and fraud detection [53]. The regulatory frameworks, such as PSD2 in Europe, drive open banking initiatives, which empower banks and third-party providers for a more integrated financial service [54].
Secondly, cybersecurity also needs to be enhanced in protecting sensitive customer data, which is prone to growing digital threats, so that trustworthy digital banking platforms can be trusted [55]. It also affirms many of the regional differences regarding digital transformation strategies. In the case of North America, banks primarily concentrate on nurturing advanced mobile banking solutions and adopting the use of AI (artificial intelligence) technologies to optimise customer experience and reduce intricacies during operations [56]. In Europe, such regulatory initiatives as PSD2 have sped up the adoption of open banking models, developing work together with competing within the financial ecosystem [54]. The contrast regarding Asia can be found with respect to the rapid adoption of mobile banking solutions, ascribing to the high smartphone penetration rates and a tech-savvy population [57].
Infrastructure limitations characterise emerging markets and are complemented, especially in those having the financial inclusion potential through mobile technologies, with opportunities to deliver financial services to underserved populations [58]. Digital transformation trends in the recent past further point out how banks are adopting innovative technologies to keep abreast. Ever-increasing adoption is cloud banking is due to its capacity to reduce costs, operational efficiency and scalability [59]. Another trend is hyper-personalisation, which is being used by banks using big data analytics to provide customised products or services to individual customers to increase the satisfaction and loyalty towards the banks [60, 41]. Predictive analytics of creditworthiness and fraud detection have become AI-driven risk assessment, revolutionising the risk management practices by being able to be more accurate [52]. Together, these are an array of strategies and trends that collectively show how retail banks all over the world navigate their digital transformation journeys so they can adapt to growing customer requirements and stay in the game of a swiftly transforming financial landscape.
5. Value Creation for Customers
Digital banking can be used to create great value for customers on multiple critical frontiers, such as improving customer experience and engagement, getting better security and trust, as well as achieving higher efficiency and a more accessible banking experience. Personalised services, real-time support, and automated banking solutions help in integrating and giving a new age of experience to the customers.
According to studies, personalisation has evolved from being a convenience to being an expectation from the customers who now expect personalised experiences that match their taste and needs [61]. For example, an AI and data analytics banking would be able to provide hyper-personalised services for customers, like delivering hyper-personalised financial advice or product recommendations, for which customer satisfaction and engagement increase significantly [51]. Moreover, chatbots driven by AI deliver timely support for customer questions efficiently and enhance the overall service delivery [52].
There are enhanced security measures as well, as it is also imperative to build trust in the digital banking environment. Digital identity verification methods and blockchain technology implement a robust security framework to safeguard customers’ data at all times and keep transactions transparent [53]. With the proliferation of cyberattacks, banks are becoming more concerned about the secure giving and receiving of information through biometric and cryptographic security. Moreover, these measures protect customer data, maintain customer trust, and lead to the banking relationship [62].
Also, the digital banking services are efficient and accessible for value creation. Now, thanks to the digital transformation initiatives, the transaction times have reduced to a minimum, and customers can perform their banking activities with swift performance. Self-service banking options bring customers more power to handle their finances independently, and this boosts financial inclusion, especially in emerging markets where the traditional banking industry may not be available [58]. The trend towards enabling self-service capabilities helps banks to serve a larger audience and carry out operations that require less dependency on physical branches.
6. Challenges in Implementing Digital Transformation Strategies
Implementing digital transformation strategies in retail banking presents several challenges that can hinder progress and affect overall effectiveness. One significant barrier is technological obstacles, particularly the integration of new digital solutions with legacy systems. Many banks still rely on outdated IT infrastructures, which complicates the adoption of modern technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI). Studies indicate that a considerable percentage of financial institutions continue to operate legacy mainframes that are not designed for today’s interconnected digital environment, making it difficult to achieve seamless integration and data management [63, 64].
In addition, protecting private customer data during the use of new technologies adds challenges to the transformation process [65, 55]. Following rules and guidelines becomes a significant obstacle in the digital transformation of banks. Times for adopting new digital efforts may be slower because each country or region has its own banking regulations for financial institutions.
It is important for a company to follow these rules to maintain credibility, yet it often takes considerable time and money and can make it harder to move innovations forward [17]. So, banks should have serious compliance processes in order to meet rules while integrating new technologies. Changing the way a business operates is also often met with resistance. Some workers may be reluctant to use new technology at work, as they worry about losing their jobs or taking time to learn how the technology works [56]. Constants changing in the world of finance can make customers wary of using new banking technologies. Accomplishing this shift in culture helps support digital innovation within the organization.
Cybersecurity threats are also becoming a major issue for banks today. As banks increase their digital footprint, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. The need for enhanced cybersecurity measures is paramount, as breaches can lead to significant financial losses and damage customer trust [62]. Banks must prioritise investments in cybersecurity technologies and practices to safeguard their operations and maintain customer confidence in their digital services.
7. Proposed Framework for Improving Digital Transformation Strategies
Based on the findings from the literature, a proposed framework of digital transformation strategies in retail banking appears, towards recommendations for using such advanced technologies, deploying the best practices adopted in other countries, and policymaking recommendations toward banks and the central bank.
The main recommendation is to integrate AI-driven decision-making processes. AI technologies enable banks to increase their operational efficiency and extent of their customer service. AI can also analyse large amounts of customer data to be used to provide customised financial advice and do routine tasks, such that human employees can spend time on complex customer interaction [52].
Cloud computing is also crucial in the adoption of scalable and flexible banking operations. Osei notes in this regard that cloud platforms help unite the new technologies seamlessly and cut down on infrastructure costs, including costs related to updates, maintenance, and support of infrastructure [59].
It also includes customer-centric design as a fundamental essence. In this approach, it focuses on customer journeys, mapping out touchpoints and improvement areas so that every online or digital initiative sets its priority as enhancing consumer experience [66]. If banks want to encourage their clients to be more engaged and satisfied, they need to concentrate on a user-friendly interface and easy-to-use services.
By looking at best practices from various countries, one can find out how to successfully go about a digital transformation [68]. To exemplify, the FinTech processes have been identified to be robust in Singapore as it has been successful in having a robust regulatory environment, which allows for banks to work with technology providers in a given cooperation [67].
Open banking models are adopted by banks in the UK and the USA that promote competition and increase customer choice through third-party integrations [54]. Similarly, another such critical example is the UAE, where banks have extensively adopted digital transformation in all operations through the use of advanced technologies to improve customer engagement [61].
Through these international examples, we can see how different approaches will bear greatly positive effects when it comes to operational effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
In addition, it is important to provide policy recommendations for banks as well as for regulators to support the proposed framework. For employees and customers to use digital banking platforms with ease, digital literacy is a critical attribute to employ as it helps to strengthen the digital literacy of every stakeholder.
Through training programs which help employees improve digital skills and customers understand how to safely use digital services, employees will be able to adapt to new technologies [56]. Additionally, there are positive attempts to collaborate with FinTech companies for innovation and better service delivery. Financial institutions can leverage the newest technologies and foster partnerships between them and FinTech firms to work efficiently when meeting the changing consumer demands [69].
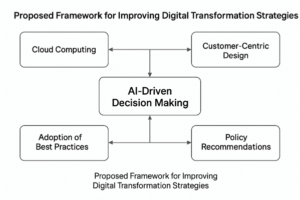
Figure 1: Proposed Framework
8. Future Research Directions
The online revolution of banking has many avenues of future research, the majority of which are core areas that will enhance the level of knowledge and hasten the adoption of an innovation strategy [70]. An important direction of further research is to extend the research to investment banking, as one important avenue for exploration. Despite the focus of current literature toward consumer-facing services, investment banks have unique challenges and opportunities in the transformation of the digital environment. Such digital technologies can potentially help in optimising trading processes, managing risk, and engaging with clients in the investment banking landscape [55].
Future work is also likely to be applied to the uses of quantum computing in optimising banking security. Cyber threat continues to evolve into more sophisticated forms; the traditional encryption may not be enough. One of the applications of quantum computing is that quantum encryption techniques could provide a way for banks to secure sensitive information at an unprecedented level [71]. As quantum computing evolves, it will be essential to explore how quantum computing can be exploited in banking security protocols and make sense in current systems.
Secondly, the application of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) globally is an important piece of research [72]. Further, for many central banks, CBDCs are currently either on the corporate road map or being tested and piloted; therefore, there is a need to understand how these technologies will impact monetary policy and financial stability, as well as the behaviour of consumers. There could be research on how CBDCs would reconfigure the payment system, aid financial inclusion, or affect the competitive forces in the space between traditional banks and digital currencies [73].
9. Conclusion
This review presents a global trend, challenges, and opportunities based on digital transformation strategies in retail banking. The review synthesises results from multiple studies by offering the idea of how AI, blockchain, open banking, and cloud technologies are helping in the process of boosting banking efficiency as well as customer experience.
Even though there is no debate about the advantages, there are obstacles such as outdated infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and the persistent problem of cybersecurity. Challenges in these cases are suggested to be overcome by applying AI-driven decision-making and improved cybersecurity strategies, as well as better collaboration between banks and FinTechs.
In addition, global best practices illustrate how financial institutions based in the leading economies have effectively included digital innovations into work processes, providing banks worldwide with examples.
Future developments in banking security and operational effectiveness should arise from technologies emerging that are already on the brink of replacing banking systems—such as CBDCs, quantum computing, and other similar technologies. With ongoing change in banking, digital transformation, a targeted approach to innovation, security, and regulation will be important to preserve competitive advantage and best serve the customers by improving financial services.
References
[1] Adewumi A, Ewim SE, Sam-Bulya NJ, Ajani OB. Advancing business performance through data-driven process automation: A case study of digital transformation in the banking sector. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Updates. 2024;8(02).
[2] Agarwal M. THE ROLE OF FINTECH IN DISRUPTING TRADITIONAL BANKING
MODELS. UNIFIED VISIONS. 2024 Nov 15;260.
[3] Faisal NA, Nahar J, Waliullah M, Borna RS. The Role Of Digital Banking Features In Bank Selection An Analysis Of Customer Preferences For Online And Mobile Banking. Frontiers in Applied Engineering and Technology. 2024;1(01):41-58.
[4] Benali S, Boumenkar D. Contribution of Chatbot Applications to Attaining Digital Financial Inclusion-Analysis and Evaluation of America’s Chatbot Erica Experience. ةلجم
ثوحب ةرادلإا داصتقلااو. 2024 Nov 1;6(3):497-516.
[5] Eccles RG, Krzus MP. Constructing Bank of America’s 2017 Mock Integrated Report:
Experiment No. 3. Available at SSRN 3226953. 2018 Aug 6.
[6] Al Nuaimi MA. An Omnichannel Digital Banking Platform for Smart City Services: A UAE Case Study (Doctoral dissertation, The British University in Dubai).
[7] Vittala KP, Ahmad SS, Seranmadevi R, Tyagi AK. Emerging technology adoption and applications for modern society towards providing smart banking solutions. InEnhancing medical imaging with emerging technologies 2024 (pp. 315-329). IGI Global.
[8] Bankuoru Egala S, Boateng D, Aboagye Mensah S. To leave or retain? An interplay between quality digital banking services and customer satisfaction. International journal of bank marketing. 2021 Oct 28;39(7):1420-45.
[9] Kaur SJ, Ali L, Hassan MK, Al-Emran M. Adoption of digital banking channels in an emerging economy: exploring the role of in-branch efforts. Journal of Financial Services Marketing. 2021 Feb 17;26(2):107.
[10] Zouari G, Abdelhedi M. Customer satisfaction in the digital era: evidence from Islamic banking. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship. 2021 Dec;10:1-8.
[11] Abdullah M. THE CUTTING EDGE TECHNOLOGIES IN COMPUTER SCIENCE: A REVIEW. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science. 2023 Jan 1;14(1).
[12] Alsemaid OM, Atri P, Kande SK, Lembhe P. Cutting-Edge Innovations in Technology and Security. Cari Journals USA LLC; 2024 Jul 12.
[13] Kaur J, Gill NS. Artificial Intelligence and deep learning for decision makers: a growth hacker’s guide to cutting edge technologies. BPB Publications; 2019 Dec 28. https://sciindex.org/category/journal-of-strategic-business/ Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
[14] Hosen MS, Islam R, Naeem Z, Folorunso EO, Chu TS, Al Mamun MA, Orunbon NO. Data-driven decision making: Advanced database systems for business intelligence. Nanotechnology Perceptions. 2024;20(3):687-704.
[15] Naimi-Sadigh A, Asgari T, Rabiei M. Digital transformation in the value chain disruption of banking services. Journal of the Knowledge Economy. 2022 Jun;13(2):1212-42.
[16] Zhao Q, Tsai PH, Wang JL. Improving financial service innovation strategies for enhancing china’s banking industry competitive advantage during the fintech revolution: A Hybrid MCDM model. Sustainability. 2019 Mar 7;11(5):1419.
[17] Gomber, P., Kauffman, R. J., Parker, C., & Weber, B. W. (2018). On the fintech revolution: Interpreting the forces of innovation, disruption, and transformation in financial services. Journal of management information systems, 35(1), 220-265.
[18] Murinde V, Rizopoulos E, Zachariadis M. The impact of the FinTech revolution on the future of banking: Opportunities and risks. International review of financial analysis. 2022 May 1;81:102103.
[19] Ofosu-Ampong K. Determinants, barriers and strategies of digital transformation adoption in a developing country Covid-19 era. Journal of Digital Science. 2021;3(2):67-83.
[20] Ononiwu MI, Onwuzulike OC, Shitu K. The role of digital business transformation in enhancing organizational agility. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews. 2024;23(3):285-308.
[21] Atabey A. Open banking & banking-as-a-service (BaaS): a delicate turnout for the
banking sector. Global privacy law review. 2021 Feb 1;2(1):59-82.
[22] Ghosh A, Mukhopadhyay I, Chakraborty S. Design and Architectural Implementation of Consortium Blockchain Based Framework for Open Banking Customer Consent and Data Handling. SN Computer Science. 2024 Feb 15;5(2):271.
[23] Kumar S. INTEGRATING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) into CORPORATE GOVERNANCE SYSTEMS. EDPACS. 2024 Dec 1;69(12):28-51.
[24] Bellantuono N, Nuzzi A, Pontrandolfo P, Scozzi B. Digital transformation models for the I4. 0 transition: Lessons from the change management literature. Sustainability. 2021 Nov 23;13(23):12941.
[25] Brunetti F, Matt DT, Bonfanti A, De Longhi A, Pedrini G, Orzes G. Digital transformation challenges: strategies emerging from a multi-stakeholder approach. The TQM Journal. 2020 Jul 21;32(4):697-724.
[26] Imran F, Shahzad K, Butt A, Kantola J. Digital transformation of industrial organizations: Toward an integrated framework. Journal of change management. 2021 Oct 2;21(4):451-79.
[27] Wansleben L. The rise of central banks: State power in financial capitalism. Harvard University Press; 2023 Jan 10. https://sciindex.org/category/journal-of-strategic-business/Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
[28] Bisri A, Putri A, Rosmansyah Y. A systematic literature review on digital transformation in higher education: Revealing key success factors. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (Online). 2023;18(14):164.
[29] Yusif S, Hafeez-Baig A. Evidence-based Information Systems (IS) research: the case of systematic literature review (SLR). Authorea Preprints. 2024 Jan 31.
[30] Klein VB, Todesco JL. COVID‐19 crisis and SMEs responses: The role of digital transformation. Knowledge and process management. 2021 Apr;28(2):117-33.
[31] Kraus S, Jones P, Kailer N, Weinmann A, Chaparro-Banegas N, Roig-Tierno N. Digital transformation: An overview of the current state of the art of research. Sage Open. 2021 Sep;11(3):21582440211047576.
[32] Tekic Z, Koroteev D. From disruptively digital to proudly analog: A holistic typology of digital transformation strategies. Business Horizons. 2019 Nov 1;62(6):683-93.
[33] Mbama CI, Ezepue PO. Digital banking, customer experience and bank financial performance: UK customers’ perceptions. International journal of bank marketing. 2018 Apr 3;36(2):230-55.
[34] Nadkarni S, Prügl R. Digital transformation: a review, synthesis and opportunities forfuture research. Management review quarterly. 2021 Apr;71:233-341.
[35] Kronblad C. How digitalization changes our understanding of professional service firms. Academy of Management Discoveries. 2020 Sep;6(3):436-54.
[36] Bhuiyan MR. Examining the digital transformation and digital entrepreneurship: A PRISMA based systematic review. Pakistan Journal of Life and Social Sciences. 2024;22(1):1136-50.
[37] Panke D. Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social
sciences.
[38] Christou PA. How to use thematic analysis in qualitative research. Journal of Qualitative Research in Tourism. 2022 Dec 1;3(2):79-95.
[39] Koroleva E. FinTech Business Models and Their Linkages with Customers and Founders.
[40] Ahmad M. Review of the technology acceptance model (TAM) in internet banking and mobile banking. International Journal of Information Communication Technology and Digital Convergence. 2018 Jun;3(1):23-41.
[41] Chauhan S, Akhtar A, Gupta A. Customer experience in digital banking: a review and future research directions. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences. 2022 May 3;14(2):311-48.
[42] Sugiarno Y, Novita D. Resources-based view (RBV) as a strategy of company competitive advantage: a literature review. InInternational Conference On Economics Business Management And Accounting (ICOEMA) 2022 Aug 15 (Vol. 1, pp. 656-666). https://sciindex.org/category/journal-of-strategic-business/ Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
[43] Donnellan J, Rutledge WL. A case for resource‐based view and competitive advantage in banking. Managerial and Decision Economics. 2019 Sep;40(6):728-37.
[44] Rane N. Enhancing customer loyalty through Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data technol
[45] Wewege L, Lee J, Thomsett MC. Disruptions and digital banking trends. Journal of Applied Finance and Banking. 2020 Nov 1;10(6):15-56.
[46] Javaid M, Haleem A, Singh RP, Suman R, Khan S. A review of Blockchain Technology applications for financial services. BenchCouncil transactions on benchmarks, standards and evaluations. 2022 Jul 1;2(3):100073.
[47] Davradakis E, Santos R. Blockchain, FinTechs and their relevance for international financial institutions (928614184X). Retrieved from. 2019.
[48] Shaikh AA, Glavee-Geo R, Karjaluoto H, Hinson ER. Marketing and Mobile Financial Services.
[49] Garg P, Srivastava T, Goel A, Gupta N. Accelerating Financial Inclusion in Developingm Economies (India) Through Digital Financial Technology. InAI-Driven Decentralized Finance and the Future of Finance 2024 (pp. 201-224). IGI Global.
[50] Ahmed G, Al Amiri N, Abudaqa A. Strategic leadership and economic transformation:The United Arab Emirates (UAE) model. Journal of Global Business Research and Practice. 2024;1(1).
[51] Shanti R, Avianto W, Wibowo WA. A systematic review on Banking Digital Transformation. Jurnal Administrare: Jurnal Pemikiran Ilmiah Dan Pendidikan Administrasi Perkantoran. 2022 Jul;9(2):3.
[52] Li Y, Yi J, Chen H, Peng D. Theory and application of artificial intelligence in financial industry. Data Science in Finance and Economics. 2021;1(2):96-116.
[53] Treiblmaier H, Beck R, editors. Business transformation through blockchain. Cham, Switzerland: Palgrave Macmillan; 2019.
[54] Eyers D. Open banking: Implications for the financial landscape. J Payments Strategy Syst. 2019;13(1):56–68.
[55] Avianto W, Siregar H, Ratnawati A, Siregar ME. Determinants of digital bank transformation: a systematic literature review with prisma and bibliometrics. JPPI (Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Indonesia). 2024 Nov 4;10(4):296-307.
[56] Diener F, Špaček M. Digital transformation in banking: A managerial perspective on
barriers to change. Sustainability. 2021 Feb 13;13(4):2032.
[57] Shaikh AA, Karjaluoto H. Mobile banking and financial inclusion: A systematic review. J Bus Res. 2015;68(3):545–56. https://sciindex.org/category/journal-of-strategic-business/Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
[58] Ozili PK. Financial inclusion in banking: A literature review and future research directions.
[59] Osei LK, Cherkasova Y, Oware KM. Unlocking the full potential of digital transformation in banking: a bibliometric review and emerging trend. Future Business Journal. 2023 Jul 7;9(1):30.
[60] Coelho L, Cachola G. Hyper-personalisation: Inducing behaviours through data—how machine learning and automation can help customers make valuable and informed decisions. Journal of Digital Banking. 2023 Jan 1;8(3):198-209.
[61] Kothari U, Grandhi B, Thrassou A. Digital transformation of retail banking in the United Arab Emirates. Journal of Asia Business Studies. 2025 Jan 23;19(1):163-81.
[62] Tanda A, Schena CM, Tanda A, Schena CM. The regulatory framework and initiatives. FinTech, BigTech and Banks: Digitalisation and Its Impact on Banking Business Models. 2019:83-100.
[63] Vanaparthi NR. The Roadmap to Mainframe Modernization: Bridging Legacy Systems with the Cloud.
[64] Gajula S. ARCHITECTURAL TRANSFORMATION OF LEGACY FINANCIAL SYSTEMS: A FRAMEWORK FOR MICROSERVICES, CLOUD, AND API INTEGRATION.
[65] Davis FD. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS quarterly. 1989 Sep 1:319-40.
[66] Best J. Breaking Digital Gridlock,+ Website: Improving Your Bank’s Digital Future by Making Technology Changes Now. John Wiley & Sons; 2018 Mar 13.
[67] Boot, A., Hoffmann, P., Laeven, L. and Ratnovski, L., 2021. Fintech: what’s old, what’s new?. Journal of financial stability, 53, p.100836.
[68] Kitsios F, Giatsidis I, Kamariotou M. Digital transformation and strategy in the banking sector: Evaluating the acceptance rate of e-services. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity. 2021 Sep 21;7(3):204.
[69] Offiong UP, Szopik-Depczyńska K, Cheba K, Ioppolo G. FinTech as a digital innovation in microfinance companies–systematic literature review. European Journal of Innovation Management. 2024 Dec 16;27(9):562-81.
[70] Munira MS. Digital transformation in banking: A systematic review of trends, technologies, and challenges. TECHNOLOGIES, AND CHALLENGES (January 27, 2025). 2025 Jan 27.
[71] Zornetta A. Quantum-safe global encryption policy. International Journal of Law and Information Technology. 2024;32(1):eaae020.
[72] Ozili PK. Central bank digital currency research around the World: a review of literature. Journal of Money Laundering Control. 2023 Mar 2;26(2):215-26. https://sciindex.org/category/journal-of-strategic-business/ Journal of Strategic Business (2025)
[73] Barney J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal of management. 1991 Mar;17(1):99-120.


